The Akkadian Civilization as the First Mesopotamian Empire
- Подробности
- 220
The Akkadian Civilization is regarded as the first great empire of the broader Mesopotamian world. Founded by Sargon of Akkad in the 24th century BC, it united the Sumerian city-states and surrounding regions under one centralized rule. The very name Akkad became synonymous with imperial power and marked a new stage in the development of Mesopotamian culture.
The Akkadian Civilization
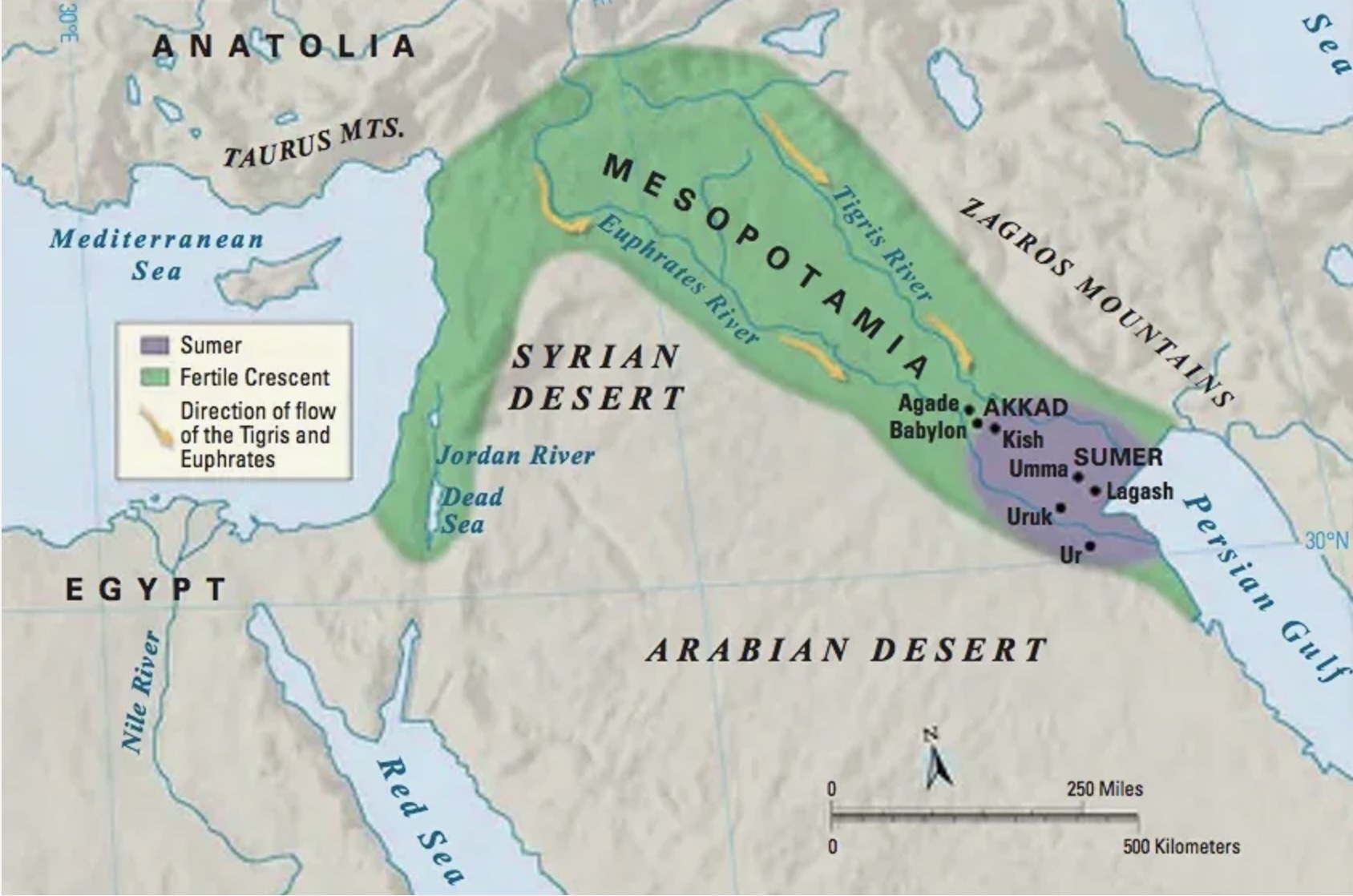
The Akkadian civilization was the first big empire in Mesopotamian history. Sargon of Akkad joined many Sumerian city-states under one ruler. The capital was Akkad, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
What did they keep from the Sumerians? They kept cuneiform writing, city temples to their gods, and canals for farming. They also used Sumerian stories and number ideas in schools and offices.
What new things did they give the world? They built the first strong central government with city governors, and set the same laws and a tax system for the whole empire. They also made one common language that many people used. Their armies and traders reached the Mediterranean coast and the Persian Gulf, which helped trade. The famous Akkadian kings were Sargon and Naram-Sin.
Why did the empire fall? It grew too big to control, there were rebellions, a long drought hurt crops, and the Gutians attacked many times. After about two hundred years, the empire ended, but its ideas about ruling, writing, and trade were inherited by later Mesopotamian civilizations, like Babylon.
LISTEN TO THE TEXT




