WHY DOES IT RAIN?
- Подробности
- 134
Rain happens because of the water cycle. First, liquid water on Earth evaporates and becomes water vapor in the air. Then this vapor condenses into clouds and later falls back as precipitation — rain, snow or hail.
WHY DOES IT RAIN?
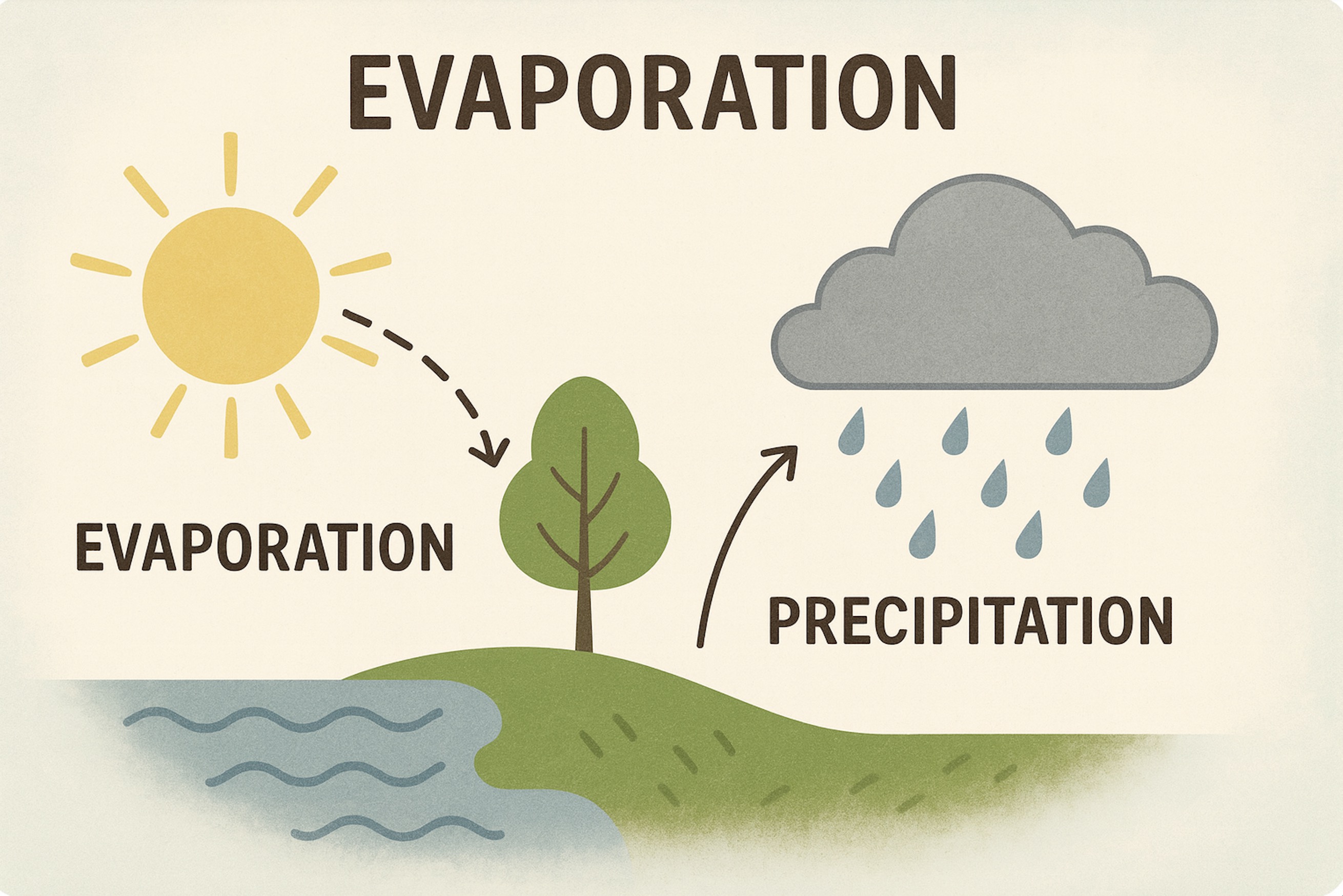
Why does it rain? 🌧
Because of the water cycle.
1. Evaporation.
Water from oceans, rivers, lakes, and soil evaporates because of the Sun’s heat. Plants also release water through their leaves.
2. Cloud formation.
Water vapor goes up into the colder parts of the air. The higher it goes, the colder the air becomes. When water vapor gets cold enough, it condenses, which means it turns into tiny water drops or ice crystals (if the temperature is below 0 °C). This is how clouds appear.
3. Growth of drops.
Tiny water drops bump into each other and join into bigger drops. If the temperature in the cloud is below zero, ice crystals appear. They also bump into each other and grow, becoming snowflakes.
When the water drops or ice become big and heavy, the rising air can no longer hold them. They fall down because of gravity as rain or snow.
A cloud can give rain far away from the place where it was made. It carries water and inside the cloud drops keep bumping, growing, and then falling as precipitation.
4. When does hail fall?
Hail forms in thunderstorm clouds. Strong updrafts (strong rising air) push and freeze small drops again and again. They grow into big ice balls. When the updraft cannot hold them anymore, they fall down as hail.
LISTEN TO THE TEXT




