SCIENCE-THE SUN
- Подробности
- 236
The Sun is the center of our Solar System. It is a hot ball of gas that gives Earth light and heat. Inside, hydrogen turns into helium and releases energy.
THE SUN
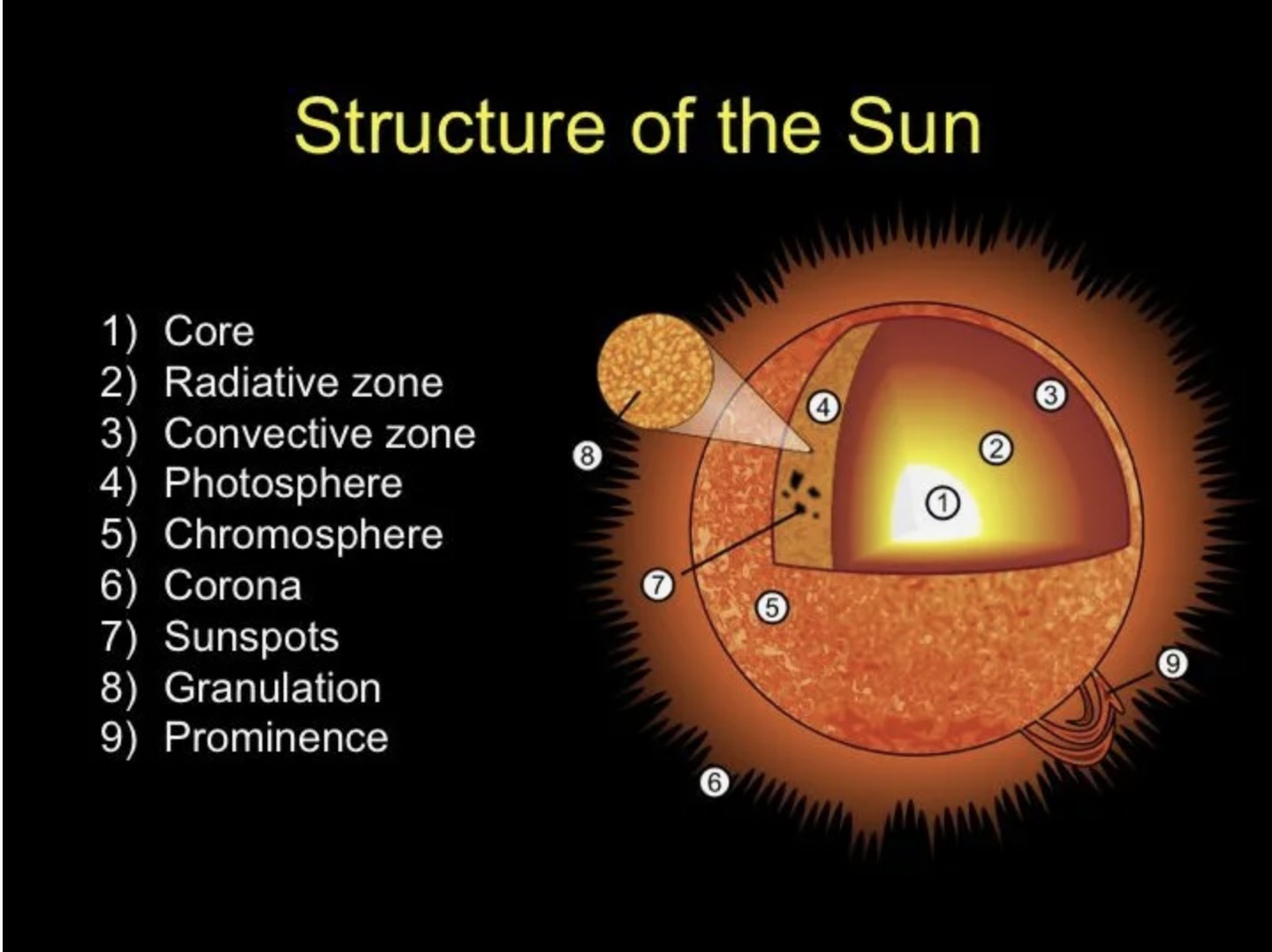
The Sun formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
The diameter of the Sun is about 1,392,000 km. If you compare it to Earth’s, which is 12,742 km, it is about 109 times wider than Earth’s.
The Sun is located in the center of our Solar System, and all the planets rotate around it. They are held by the Sun’s gravity because the Sun is the heaviest object in our Solar System, although it is considered a medium-sized star.
Without the Sun, life on Earth could not exist. It gives us light and heat. Plants use sunlight and carbon dioxide to make food for themselves. This is called photosynthesis. In turn, they become food for other animals. They also produce oxygen that animals use for breathing.
The Sun mostly consists of hydrogen and helium . Deep in the center, tiny atoms join together in a process called nuclear fusion. This makes a huge amount of energy. The energy moves from the center to the surface and then into space as light and heat.
The temperature in the center of the Sun is about 15 million °C. The temperature on the surface of the star is about 5,500 °C.
The Sun is active. It blows out a stream of charged particles called the solar wind. This wind constantly attacks Earth’s atmosphere, but our magnetic field protects it from most of the damage. We also see solar flares—bright eruptions of hot plasma and charged particles from the Sun’s atmosphere. Another form of solar activity is coronal mass ejections (CMEs)—huge blasts of magnetized plasma from the Sun’s corona that stream into space. CMEs, solar flares and high-speed solar wind streams can trigger auroras near Earth’s poles and disrupt radio signals and GPS. During strong geomagnetic storms, some people also report feeling unwell.
In the past, people studied the Sun only with telescopes. Now we send space missions—such as satellites—that fly close to the Sun and study it in detail, sending data back to Earth. The Sun is about 4.5 billion years old and has around 5 billion years left. Eventually, it will grow into a red giant, swallowing Mercury and Venus, and maybe even Earth. After that, it will lose its outer layers, and the remaining core will become a white dwarf.
LISTEN TO THE TEXT




